Crafting User-Centered Design: A Comprehensive Guide
Embark on a journey through the realm of user-centered design, where innovation meets the needs and desires of the end user. This captivating exploration delves into the core principles and practical applications that drive successful product development.
User-centered design is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental approach that places users at the heart of the design process, ensuring solutions that resonate and truly make a difference.
What is User Centered Design?
User Centered Design (UCD) is an iterative design process that focuses on the needs, wants, and limitations of end users. It involves involving users in every stage of the design process to create products that are intuitive, easy to use, and meet their needs effectively.
Examples of User Centered Design in Product Development
- Apple’s iPhone: Apple incorporates user feedback and conducts extensive usability testing to create user-friendly interfaces and features.
- Google Search: Google constantly refines its search algorithms based on user behavior and feedback to provide relevant search results.
- Tesla’s Electric Vehicles: Tesla designs its vehicles with a user-centric approach, focusing on features like autopilot and intuitive touchscreens.
Importance of Prioritizing User Needs
User needs should be prioritized in the design process to ensure that products are user-friendly, efficient, and enjoyable to use. By understanding the needs and preferences of users, designers can create products that truly meet their expectations and provide a positive user experience.
This approach can lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, the success of the product in the market.
Understanding User Needs
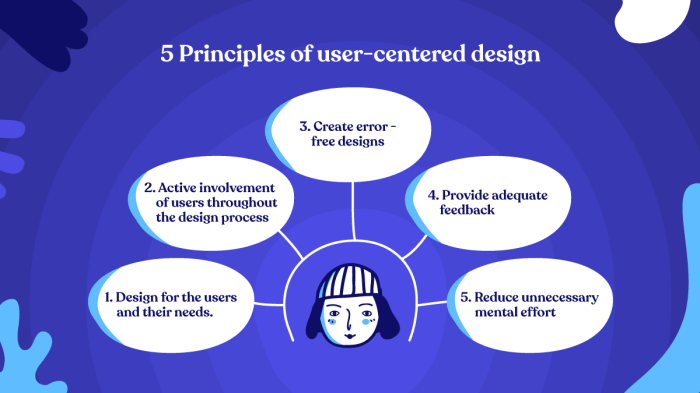
In user-centered design, it is crucial to gather feedback from users to truly understand their needs and preferences. By doing so, designers can create products and services that cater to the user’s expectations and provide a better overall experience.Empathy plays a significant role in understanding user perspectives.
By putting oneself in the user’s shoes, designers can better grasp their motivations, challenges, and desires. This empathetic approach helps in creating solutions that are truly user-centric and address real-life issues effectively.
Methods for Gathering User Feedback
- Conducting surveys and questionnaires to collect quantitative data on user preferences.
- Organizing focus groups and interviews to delve deeper into user insights and motivations.
- Observing user behavior in real-life settings to understand how they interact with products or services.
Creating User Personas
User personas are fictional representations of target users based on research and data. These personas include demographic information, goals, behaviors, and pain points of different user segments. Designers use these personas as a reference to guide their design decisions and ensure that they align with user needs and expectations.
Design Thinking Process
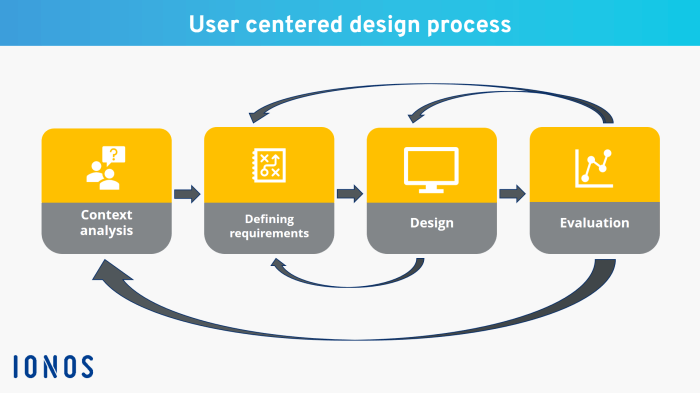
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that focuses on understanding the user’s needs and creating innovative solutions to meet those needs. It involves a series of steps that help designers empathize with users, define the problem, ideate potential solutions, prototype those solutions, and test them with users for feedback.
Steps in the Design Thinking Process
- Empathize: Understand the user’s perspective by observing and engaging with them to gather insights.
- Define: Clearly define the problem based on the user’s needs and insights gathered during the empathy phase.
- Ideate: Brainstorm and generate a wide range of creative solutions to address the defined problem.
- Prototype: Create tangible representations of the ideas generated during the ideation phase to test and refine.
- Test: Gather feedback from users by testing the prototypes to validate the solutions and make improvements.
User Centered Design in the Design Thinking Framework
User-centered design is at the core of the design thinking process as it emphasizes the importance of understanding user needs, preferences, and behaviors throughout the design journey. By placing the user at the center of the design process, designers can create more meaningful and impactful solutions that truly address user challenges and enhance their experiences.
Importance of Prototyping and Testing in User Centered Design
Prototyping and testing are essential components of user-centered design as they allow designers to bring their ideas to life in a tangible form and gather valuable feedback from users early in the design process. By prototyping and testing, designers can quickly iterate on their designs, identify potential issues, and refine the solutions to better meet user needs.
For example, creating a low-fidelity prototype of a mobile app and testing it with users can reveal usability issues that may not have been apparent in the initial concept, leading to a more user-friendly and effective final product.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a crucial step in the user-centered design process as it helps ensure that the final product meets the needs and expectations of the users. By observing real users interact with the product, designers can identify any usability issues and make necessary improvements to enhance the overall user experience.
Importance of Usability Testing
Usability testing allows designers to gather valuable feedback on the usability of a product, including navigation, layout, content, and overall user interface. By understanding how users interact with the product, designers can make informed decisions to optimize the design and address any pain points that users may encounter.
- One-on-One Testing: Involves observing individual users as they interact with the product, providing detailed insights into their behavior and preferences.
- Remote Testing: Allows designers to conduct usability tests with users located in different geographic locations, providing a broader perspective on the product’s usability.
- Expert Review: Involves usability experts evaluating the product based on best practices and industry standards, offering valuable insights for improvements.
- A/B Testing: Compares two versions of the product to determine which design performs better in terms of user engagement and satisfaction.
Influencing Design Iterations
Feedback from usability testing can significantly impact design iterations by highlighting areas for improvement and guiding design decisions. For example, if users struggle to find a specific feature during testing, designers can redesign the navigation to make it more intuitive.
Similarly, if users express confusion about a particular layout, designers can adjust the design to enhance clarity and usability.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, user-centered design stands as a beacon of customer-centric innovation, revolutionizing the way products are created and experienced. By prioritizing user needs, embracing empathy, and iteratively testing designs, businesses can pave the path to lasting success in a competitive market landscape.
FAQ Summary
What are the key principles of user-centered design?
User-centered design revolves around empathy, iterative testing, and prioritizing user needs throughout the design process.
How can user personas benefit the design process?
User personas provide a clear understanding of target users, guiding design decisions and ensuring solutions meet specific user requirements.
Why is usability testing crucial in user-centered design?
Usability testing helps identify areas for improvement, validates design choices, and ensures the final product meets user expectations.




